Companies may choose to conduct alcohol screening for various reasons. For some federally regulated workers, governing organizations mandate random alcohol screening. For other organizations, alcohol testing is more likely to be conducted after an accident, when there is evidence of intoxication at work, or for access to a job site.
The DOT has specific alcohol testing requirements for individuals and employees with a CDL, employees of the Federal Transit Authority, pilots, flight attendants, and air traffic controllers (among others). Employees who are subject to the DOT-mandated alcohol testing may be required to submit to:
- Pre-employment testing
- Random tests
- Post-accident testing
- Tests for reasonable suspicion
- Returning to duty testing after a positive test
Alcohol is legal, and the off-duty consumption of alcohol is protected. However, in many jobs, working under the influence is not only a bad idea but can be a serious safety risk. Companies should clearly communicate policies about alcohol use and testing so there is no ambiguity and testing is conducted fairly and without bias.
Why is Drug and Alcohol Screening Important?
- Safety – Alcohol slows reaction times, impairs judgment, and reduces motor skills. That means that workers under the influence who are driving or operating machinery are a safety hazard to themselves or others.
- Legal Compliance – For some industries, such as commercial transportation, the federal government mandates workplace alcohol testing, and employers must conduct regular testing to avoid fines or penalties.
- Workplace Culture and Productivity—Organizations want to create a safe, professional, productive, and healthy workplace. Enforcing workplace sobriety policies can help create that kind of positive culture.
Types of Alcohol Testing
There are several ways to test for alcohol consumption and impairment, each with its benefits and drawbacks.
Breath Test
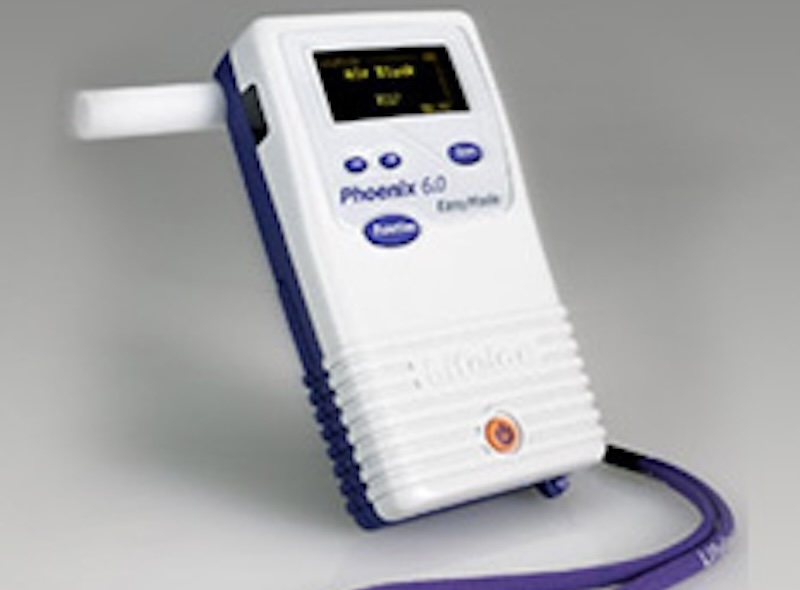
Breath alcohol testing is the most common method used in the workplace because it is accurate, quick, noninvasive, and provides immediate results. Employers just need an Evidential Breath Test device (EBT), which is portable and easily administered on-site. The DOT primarily uses evidential breath alcohol testing devices, which can be administered immediately following an accident or traffic incident. It also mandates EBT for confirmatory tests following a positive screening test.
For a breath test, the employee blows into a breathalyzer. The device measures the amount of alcohol in a person’s breath, the breath alcohol level (BrAC), which is equivalent to the amount in their blood.
The legal blood alcohol limit for driving is .08 in most states, but for CDL drivers, a reading of .02 is positive, and .04 is a serious violation. The DOT requires that individuals administering alcohol testing have proper training in the device used for the testing.
Saliva Test
Saliva testing is another method of testing breath alcohol levels approved by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). Saliva testing is non-invasive, accurate, and more resistant to tampering than urine tests.
Test administrators collect a saliva sample by either swabbing the mouth or using a specialized device. The sample may have to be sent to a lab for results, although the DOT has approved some instant result tests. The instant saliva screening devices can be used to rule out alcohol impairment, but any positive test has to be confirmed with an EBT alcohol test.
Blood Test
Blood alcohol testing measures the amount of alcohol in an individual’s bloodstream. Because it is an intrusive method that must be conducted by a health care professional or a laboratory, it is not commonly used for workplace alcohol testing. However, the Federal Railroad Administration requires blood alcohol testing after any railroad accident.
Blood alcohol testing is more accurate than breath or urine tests, but the results can be invalid if the lab does not handle the sample properly.
Urine Test
Urine testing is generally not recommended for workplace alcohol testing and is not an approved screening test by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. Urine testing is done by collecting a urine sample from an employee and then sending it to a lab for analysis. At the lab, technicians will use a urine analyzer to determine if there is alcohol or metabolites in the sample.
Urine testing is not very accurate, as alcohol doesn’t show up in urine for two hours and can be detected in a urine sample up to 24 hours after consumption. So, an employee could have a couple of beers over the weekend and still test positive in a urine sample on Monday. Urine testing can also generate false positives for individuals with medical conditions such as diabetes.
Urine testing is also susceptible to tampering. Unlike other tests, individuals can forge a urine test by diluting or swapping the sample. Even with temperature testing, it is hard for employers or courts to prove that a sample is invalid.
EtG Test
There is a difference between a urine test and an EtG test. EtG tests, or ethyl glucuronide tests, are becoming increasingly popular as an alternative urine test. While a urine test measures actual alcohol (ethanol) in the blood, an EtG test measures the amount of ethyl metabolite. EtG can detect recent alcohol consumption, even before a traditional ethanol test shows up positive. EtG testing can be used in combination with drug testing, eliminating the need for employers to collect multiple samples.
An EtG test has an 80-hour detection window, meaning that an employee can test positive days after consuming alcohol. The test is also susceptible to false positives created by alcohol in common household products such as hairspray, deodorant, mouthwash, cleaning products, or even small amounts of alcohol in food.
Both ethanol and EtG urine tests are generally used to verify complete abstinence if that has been court-ordered or mandated by an employer.
How to Get Tested
While some employers may choose to conduct alcohol screening in-house, federally regulated industries have requirements about where employees can go for random testing and how post-accident testing must be conducted. If you are thinking, “How do I find a DOT breath alcohol testing and physical exam near me?” try TeamCME. They have an easy-to-use database of qualified DOT medical examiners, so you can find something convenient whether you are at home or on the road.