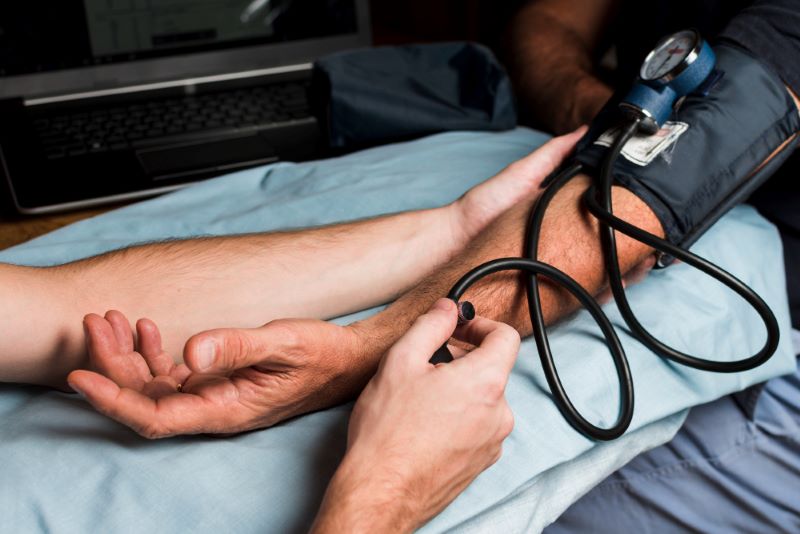
7 Factors That Can Affect Blood Pressure During DOT Physical
If you have your commercial driver’s license (CDL), you may need a physical exam. Your blood pressure is a vital aspect of the physical and an important indicator of your health. Untreated high or low blood pressure can lead to avoidable accidents, so it’s important to know your blood pressure is within the acceptable range.
If you don’t have any worrisome health indications, the medical examiner can clear you for two years. Your blood pressure must be below 140/90 for this result. However, if your blood pressure is above that cut-off, you will have a shorter recheck period to get it back under control through lifestyle modifications, medications, or both.
The examiner must disqualify you if your blood pressure exceeds 179 (the top number) or 110 (the bottom number). This is considered stage three hypertension and you are at immediate risk of having a heart attack or stroke. You will need to reduce your blood pressure below 140/90 before you will be able to be medically certified. Once you have had stage three hypertension, you will be limited to six month certification periods.
Beyond diagnosable hypertension, there are many reasons your blood pressure could be high on the day of your Department of Transportation (DOT) exam. Review the following seven factors affecting blood pressure readings:
1. Anxiety or Stress
Your emotional state plays a significant role in your blood pressure. If you are anxious or stressed, your fight-or-flight nervous system kicks in, boosting your blood pressure for the potential danger.
Some patients have white coat syndrome, where merely being in a doctor’s office stresses them out. With or without the actual presence of a white coat, your blood pressure may shoot up in a clinic or hospital environment. Typically, taking your blood pressure at the end of your physical exam is enough time to allow it to settle back to your normal range.
2. Stimulant Consumption
Caffeine and nicotine are the most common stimulants that raise your blood pressure. At the very least, you should avoid them within a few hours of your exam. Avoid coffee, tea, soda, energy drinks, smoking, vaping, or chew, one to two days before your physical to get an accurate blood pressure reading.
Stimulants can also affect your ability to get enough deep, restorative sleep. Being overly tired can increase your blood pressure as well. Ensure you’re well rested before your exam for your blood pressure’s sake.
3. Physical Activity
You shouldn’t plan to go to a physical straight from the gym or after high-intensity exercise. Even bounding up the stairs or rushing in late from the parking lot can spike your blood pressure temporarily. Keep your heart rate and blood pressure low by arriving at your appointment with plenty of time. Take deep, steadying breaths and walk to avoid any inaccurate readings.
4. Discomfort
If you already know what to expect with a DOT exam, you know you need to provide a urine sample. If you have a full bladder during the blood pressure measurement, it can increase your reading. Request to provide your urine sample before the physical exam so you are comfortable and get an accurate reading.
Practitioners’ offices are often chilly. The cold environment causes your blood vessels to constrict since your body is tightening up. This will temporarily elevate your blood pressure. Wear layers to avoid this phenomenon if it’s winter or you cool quickly.
5. Talking, Movement, and Positioning
Your blood pressure reading will change if you are talking, holding your breath, or crossing your legs or ankles. The same will happen if you are holding your arm up or are tensing it with the cuff on. The blood pressure reading is most accurate when you are:
- Sitting quietly with your back supported
- Breathing regularly
- Relaxed, especially the limb with the blood pressure cuff
- Planting your feet flat on the floor
6. Cuff Size
The nurse should use an appropriate-sized cuff to measure your blood pressure. One that is too big or too little will lead to inaccurate readings. If your blood pressure is abnormal and the cuff barely fits around your arm or has excess material left over, ask for the appropriate cuff change and a remeasurement.
Take note of the correct cuff size to request it for future appointments. Always have the cuff directly on your skin instead of over your clothing. This will help ensure you have the correct cuff size and the most accurate measurement.
7. Medical Conditions and Medications
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, decongestants, and prescription medications can affect blood pressure. Let your provider know all your medications and supplements, as they may change your blood pressure readings.
Beyond blood pressure conditions, if you have any of the following conditions, they could impact your blood pressure:
- Diabetes
- Kidney disease
- Thyroid disorders
- Heart conditions
- Endocrine disorders
- Sleep apnea
Being overweight can put extra strain on your heart and blood vessels. Over time, this can contribute to developing the above conditions, increasing your blood pressure. Ensure you eat a diet low in salt, processed sugar, and saturated fats found mainly in fatty meats. Eat a diet rich in fresh foods, including fruit, vegetables, eggs, low-fat dairy, and lean meats. Drink plenty of water. Aim to get 30 minutes of low to moderate-intensity exercise daily; walking around truck stops counts. Your body, blood pressure, and overall health will be better for your efforts.